这篇博文重点讲状态依赖的最短路问题
状态依赖的SPFA算法
电梯调度问题
( x , j ) (x, j) ( x , j ) x x x j j j spfa queue statues \text{spfa queue statues} spfa queue statues : = v i s ( x , j ) := vis(x, j) : = v i s ( x , j )
for ∀ i ∈ [ 1 , m ] ↔ next position \textbf{for}\ \forall i \in [1, m] \leftrightarrow \text{next position} for ∀ i ∈ [ 1 , m ] ↔ next position ~~~~~~ w = ∣ i − j ∣ + 2 ∣ C ( i ) ∣ w=|i-j|+2|C(i)| w = ∣ i − j ∣ + 2 ∣ C ( i ) ∣
d ( x + C [ i ] , i ) = min { d ( x + C [ i ] , i ) , d ( x , j ) + w } run spfa() \begin{gathered}
d(x+C[i], i) = \min\{d(x+C[i],i), d(x,j)+w\} \\ \ \\
\text{run spfa()}
\end{gathered}
d ( x + C [ i ] , i ) = min { d ( x + C [ i ] , i ) , d ( x , j ) + w } run spfa()
spfa算法注意点 在计算下一个状态的时候 判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 if (D[next] > D[cur] + w) { if (!inq[next]) { que.push(next); inq[next] = 1; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 const int maxn = 1000 + 5; const int maxm = 20 + 5; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n, m; int D[maxn][maxm], inq[maxn][maxm]; typedef pair<int, int> PII; int C[maxn]; // == run spfa == void initSpfa Set(inq, 0); Set(D, inf); } void spfa(int st_x, int st_j) { queue<PII> que; que.push(MPR(st_x, st_j)); D[st_x][st_j] = 0; inq[st_x][st_j] = 1; while (!que.empty()) { int x = que.front().first; int j = que.front().second; que.pop(); inq[x][j] = 0; _rep(i, 1, m) { int nx = x + C[i]; int w = abs(i - j) + 2 * abs(C[i]); if (nx < 1 || nx > n) continue ; if (D[nx][i] > D[x][j] + w) { D[nx][i] = D[x][j] + w; if (!inq[nx][i]) { que.push(MPR(nx, i)); inq[nx][i] = 1; } } } } } // == spfa finsihed == int main freopen("input.txt" , "r" , stdin); scanf("%d%d" , &n, &m); int pos = 0; _rep(i, 1, m) { scanf("%d" , &C[i]); if (C[i] == 0) pos = i; } // then spfa initSpfa(); spfa(1, pos); int ans = inf; _rep(i, 1, m) ans = min(ans, D[n][i]); if (ans == inf) puts("-1" ); else printf ("%d\n" , ans); }
floyd路径统计
algorithm
c ( i , j ) c(i, j) c ( i , j ) i → j i \rightarrow j i → j
for ∀ e ( u , v ) ∈ E ( G ) \textbf{for} \ \forall e(u, v) \in E(G) for ∀ e ( u , v ) ∈ E ( G ) ~~~~~~ init : c ( u , v ) = 1 \text{init}: \ c(u, v) = 1 init : c ( u , v ) = 1
if d ( u , v ) > d ( u , k ) + d ( k , v ) \textbf{if} \quad d(u,v) > d(u, k) + d(k, v) if d ( u , v ) > d ( u , k ) + d ( k , v ) ~~~~~~ c ( u , v ) = c ( u , k ) ⋅ c ( k , v ) c(u, v) = c(u, k) \cdot c(k, v) c ( u , v ) = c ( u , k ) ⋅ c ( k , v )
if d ( u , v ) = d ( u , k ) + d ( k , v ) \textbf{if} \quad d(u, v) = d(u, k) + d(k, v) if d ( u , v ) = d ( u , k ) + d ( k , v ) ~~~~~~ c ( u , v ) + = c ( u , k ) ⋅ c ( k , v ) c(u, v) += c(u, k) \cdot c(k, v) c ( u , v ) + = c ( u , k ) ⋅ c ( k , v )
经过 k k k floyd \textbf{floyd} floyd ∀ ( i , j ) , i ≠ j , d ( i , j ) = d ( i , k ) + d ( k , j ) \forall (i, j), i \neq j, \quad d(i,j) = d(i,k)+d(k, j) ∀ ( i , j ) , i = j , d ( i , j ) = d ( i , k ) + d ( k , j )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 const int maxn = 100 + 10; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n, m; int d[maxn][maxn]; ll c[maxn][maxn]; double ans[maxn]; void initFloyd Set(d, inf); _rep(i, 0, n) d[i][i] = 0; Set(c, 0); Set(ans, 0.0); } void floyd _rep(k, 1, n) _rep(i, 1, n) _rep(j, 1, n) { if (i != j && k != i && k != j) { if (d[i][j] > d[i][k] + d[k][j]) { d[i][j] = d[i][k] + d[k][j]; c[i][j] = 1ll * c[i][k] * c[k][j]; } else if (d[i][j] == d[i][k] + d[k][j]) { c[i][j] += 1ll * c[i][k] * c[k][j]; } } } } void solve _rep(k, 1, n) _rep(i, 1, n) _rep(j, 1, n) { if (i != j && k != i && k != j) { if (d[i][j] == d[i][k] + d[k][j]) { ans[k] += (double) c[i][k] * c[k][j] / c[i][j]; } } } _rep(i, 1, n) printf ("%.3lf\n" , ans[i]); } int main freopen("input.txt" , "r" , stdin); scanf("%d%d" , &n, &m); initFloyd(); _for(i, 0, m) { int x, y, z; scanf("%d%d%d" , &x, &y, &z); d[x][y] = d[y][x] = z; c[x][y] = c[y][x] = 1ll; } floyd(); solve(); }
Dijkstra和DAG上的dp
algorithm \textbf{algorithm} algorithm
run dijkstra() \text{run dijkstra()} run dijkstra() ~~~~~~ we get ∀ u , D(u) \textbf{we}\ \textbf{get} \ \forall u, \ \textbf{D(u)} we get ∀ u , D(u) dp ( s t ← e d ) , begin: consider ed \textbf{dp}(st\leftarrow ed) ,\ \textbf{begin:} \ \textbf{consider} \ \textbf{ed} dp ( s t ← e d ) , begin: consider ed ~~~~~~ f ( e d ) = 1 , f ( v / e d ) = 0 f(ed) = 1, f(v/ed) = 0 f ( e d ) = 1 , f ( v / e d ) = 0 ~~~~~~ sort according to D [ u ] → o r d [ ⋯ ] , o r d 0 = e d \textbf{sort} \ \textbf{according} \ \textbf{to} \ D[u]\rightarrow ord[\cdots], \ ord_0 = ed sort according to D [ u ] → o r d [ ⋯ ] , o r d 0 = e d ~~~~~~ now D ( o r d 0 ) = 0 , D ( o r d 1 ) , D ( o r d 2 ) ↑ ⋯ \textbf{now} \ D(ord_0)=0, D(ord_1), D(ord_2) \uparrow \cdots now D ( o r d 0 ) = 0 , D ( o r d 1 ) , D ( o r d 2 ) ↑ ⋯ ~~~~~~ for ∀ x = o r d i for ∀ e ( x , y ) \textbf{for} \ \forall x = ord_i \ \textbf{for} \ \forall e(x, y) for ∀ x = o r d i for ∀ e ( x , y ) ~~~~~~ ~~~~ if D ( y ) > D ( x ) , f ( y ) + = f ( x ) \textbf{if} \ D(y) > D(x), f(y) += f(x) if D ( y ) > D ( x ) , f ( y ) + = f ( x ) ~~~~~~ ans is f ( s t ) \text{ans is } f(st) ans is f ( s t )
in this case, run dp() in every node \text{in this case, run dp() in } \textbf{every} \ \textbf{node} in this case, run dp() in every node
dp ( s t → e d ) , begin: consider dp(st, ed) \textbf{dp}(st\rightarrow ed), \textbf{begin:} \ \textbf{consider} \ \textbf{dp(st,} \ \textbf{ed)} dp ( s t → e d ) , begin: consider dp(st, ed) ~~~~~~ init set f [ ⋯ ] ← − 1 \textbf{init} \ \textbf{set} \ f[\cdots] \leftarrow -1 init set f [ ⋯ ] ← − 1 ~~~~~~ dp ( x , e d ) \textbf{dp}(x, ed) dp ( x , e d ) ~~~~~~ ~~~~ if x = e d , return 1 \textbf{if} \ x = ed, \text{return } 1 if x = e d , return 1 ~~~~~~ ~~~~ if f ( x ) ⩾ 0 , found ans, return f ( x ) \textbf{if} \ f(x) \geqslant 0, \text{found ans, return } f(x) if f ( x ) ⩾ 0 , found ans, return f ( x ) ~~~~~~ ~~~~ let f ( x ) = 0 , for ∀ e ( x , y ) \textbf{let} \ f(x) = 0, \textbf{for} \ \forall e(x, y) let f ( x ) = 0 , for ∀ e ( x , y ) ~~~~~~ ~~~~ ~~~~ if D ( y ) < D ( x ) , f ( x ) + = d p ( y , e d ) \textbf{if} \ D(y) < D(x), f(x) +=dp(y, ed) if D ( y ) < D ( x ) , f ( x ) + = d p ( y , e d ) ~~~~~~ ~~~~ return f ( x ) \text{return } f(x) return f ( x )
run dp() recursive \text{run dp() recursive } run dp() recursive
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 const int maxn = 1000 + 10; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n, m; // == Graph definition == vector<int> G[maxn]; class Edge { public: int to, weight; Edge Edge(int t, int w) : to(t), weight(w) {} }; vector<Edge> edges; void initG _for(i, 0, maxn) G[i].clear(); edges.clear(); } void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) { edges.push_back(Edge(v, w)); G[u].push_back(edges.size() - 1); } class Node { public: int u, dist; bool operator< (const Node& rhs) const { return dist > rhs.dist; } Node Node(int u, int d) : u(u), dist(d) {} }; // == Graph finished == // == dijkstra == int D[maxn], vis[maxn]; void initDij(int st) { Set(D, inf); D[st] = 0; Set(vis, 0); } void dijkstra(int st) { initDij(st); priority_queue<Node> que; que.push(Node(st, 0)); while (!que.empty()) { int x = que.top().u; que.pop(); if (vis[x]) continue ; vis[x] = 1; _for(i, 0, G[x].size()) { const Edge& e = edges[G[x][i]]; int y = e.to; if (D[y] > D[x] + e.weight) { D[y] = D[x] + e.weight; que.push(Node(y, D[y])); } } } } // == dijkstra finished == // == dp == inline bool cmp(int a, int b) { return D[a] < D[b]; } int ord[maxn]; int f[maxn]; void initDP(const int ed) { _rep(i, 1, n) ord[i] = i; sort(ord + 1, ord + 1 + n, cmp); //assert(ed == ord[1]); Set(f, 0); f[ed] = 1; } void dp(const int st) { _rep(i, 1, n) { int x = ord[i]; _for(j, 0, G[x].size()) { int y = edges[G[x][j]].to; if (D[y] > D[x]) f[y] += f[x]; } } printf ("%d\n" , f[st]); } void initDP Set(f, -1); } int dp(int x, const int ed) { if (x == ed) return 1; if (f[x] >= 0) return f[x]; f[x] = 0; _for(i, 0, G[x].size()) { int y = edges[G[x][i]].to; if (D[y] < D[x]) f[x] += dp(y, ed); } return f[x]; } // == dp finsiehd == int main freopen("input.txt" , "r" , stdin); while (scanf("%d%d" , &n, &m) == 2 && n) { initG(); _for(i, 0, m) { int x, y, z; scanf("%d%d%d" , &x, &y, &z); addEdge(x, y, z); addEdge(y, x, z); } // run dijkstra dijkstra(2); // then dp initDP(2); dp(1); //initDP(); //printf ("%d\n" , dp(1, 2)); } }
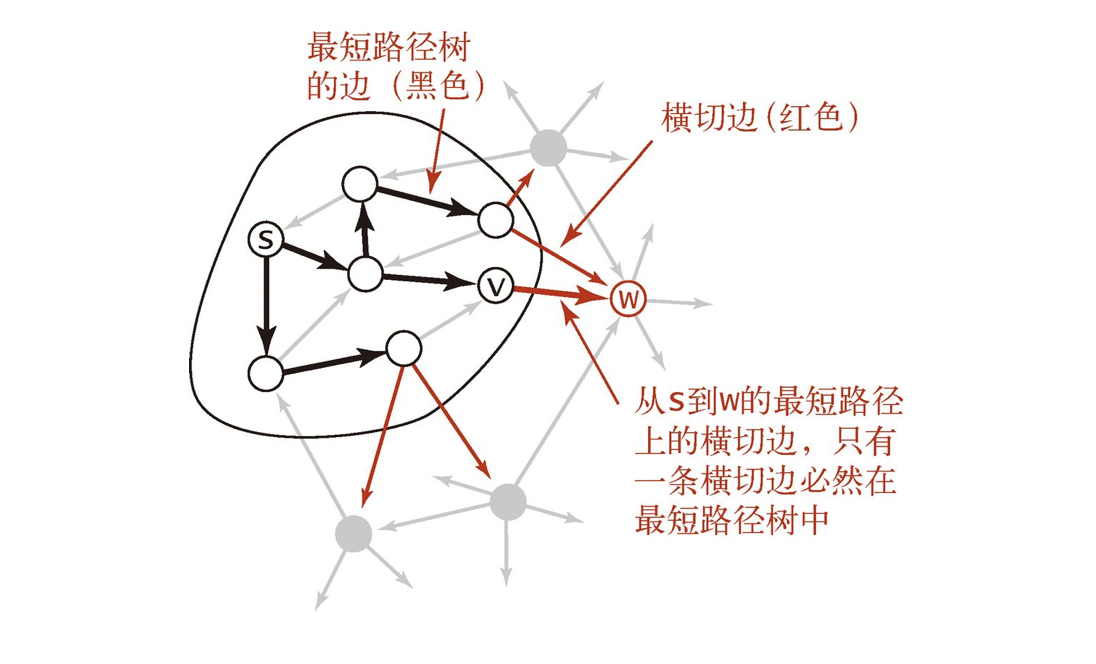
最短路树
algorithm: e ( x , u ) : = p ( u ) is the forward arc(前向弧) \textbf{algorithm:} \ e(x, u):=p(u) \ \textbf{is} \ \textbf{the} \ \textbf{forward} \ \textbf{arc(前向弧)} algorithm: e ( x , u ) : = p ( u ) is the forward arc( 前向弧 ) run d i j k s t r a ( ) and record p ( ) \textbf{run} \ dijkstra() \text{ and record } p() run d i j k s t r a ( ) and record p ( )
Dijkstra-Tree := ⋃ p ( u ) ∈ p a t h e ( p ( u ) ) \textbf{Dijkstra-Tree} \ \textbf{:=} \bigcup\limits_{p(u) \in path}e(p(u))
Dijkstra-Tree := p ( u ) ∈ p a t h ⋃ e ( p ( u ) )
init: W ( u , v ) = ⋃ w e i g h t s w ( u , v ) \textbf{init:} \quad W(u, v) = \bigcup\limits_{weights}w(u, v) init: W ( u , v ) = w e i g h t s ⋃ w ( u , v ) multiple edges, i d x ( u , v ) : = edge number \text{multiple edges, } idx(u, v) := \text{edge number} multiple edges, i d x ( u , v ) : = edge number u s e d ( s r c , u , v ) : = run dijkstra ( s r c ) , e ( u , v ) is Tree-edge or not used(src, u, v):= \text{ run dijkstra}(src), e(u, v)\text{ is Tree-edge or not} u s e d ( s r c , u , v ) : = run dijkstra ( s r c ) , e ( u , v ) is Tree-edge or not
for ∀ s r c ∈ V ( G ) \textbf{for} \ \forall src \in V(G) for ∀ s r c ∈ V ( G ) ~~~~~~ run Dijkstra ( s r c ) → mark p ( ⋯ ) \textbf{run}\ \textbf{Dijkstra}(src) \rightarrow \text{ mark } p(\cdots) run Dijkstra ( s r c ) → mark p ( ⋯ ) ~~~~~~ for ∀ u ∈ V ( G ) , ∀ e ( u , v ) ∈ Dijkstra-Tree ( G ) \textbf{for}\ \forall u \in V(G), \forall e(u, v) \in \textbf{Dijkstra-Tree}(G) for ∀ u ∈ V ( G ) , ∀ e ( u , v ) ∈ Dijkstra-Tree ( G ) ~~~~~~ ~~~~ C ( s r c ) = ∑ u D ( u ) , mark u s e d ( s r c , u , v ) C(src) = \sum_u D(u), \text{ mark } used(src, u, v) C ( s r c ) = ∑ u D ( u ) , mark u s e d ( s r c , u , v ) ans = ∑ C ( s r c ) \textbf{ans} = \sum C(src) ans = ∑ C ( s r c )
consider delete operation \textbf{consider} \ \textbf{delete} \ \textbf{operation} consider delete operation ~~~~~~ del ( u , v ) ⇒ w ( u , v ) = 0 or w ( u , v ) = W ( u , v ) [ 2 , 3 , ⋯ ] \textbf{del}(u, v)\Rightarrow w(u, v) = 0 \ \textbf{or} \ w(u, v) = W(u, v)[2, 3, \cdots] del ( u , v ) ⇒ w ( u , v ) = 0 or w ( u , v ) = W ( u , v ) [ 2 , 3 , ⋯ ] ~~~~~~ for ∀ s r c ∈ V ( G ) \textbf{for} \ \forall src \in V(G) for ∀ s r c ∈ V ( G ) ~~~~~~~~~~ if u s e d ( s r c , u , v ) = 0 , ans = ∑ C ( s r c ) \textbf{if} \ used(src, u, v)=0, \ \textbf{ans} \ = \sum C(src) if u s e d ( s r c , u , v ) = 0 , ans = ∑ C ( s r c ) ~~~~~~~~~~ else rebuild Dijkstra-Tree \textbf{else} \ \text{rebuild Dijkstra-Tree} else rebuild Dijkstra-Tree ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ run Dijkstra ( s r c ) \text{run Dijkstra}(src) run Dijkstra ( s r c ) ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ for ∀ u ∈ V ( G ) \textbf{for} \ \forall u \in V(G) for ∀ u ∈ V ( G ) ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ ans = ∑ D ( u ) \textbf{ans} = \sum D(u) ans = ∑ D ( u )
reset w ( u , v ) = W ( u , v ) [ 0 ] \textbf{reset} \ w(u, v) = W(u, v)[0] reset w ( u , v ) = W ( u , v ) [ 0 ]
UVA1416
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 const int maxn = 100 + 10; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n, m, L; vector<int> W[maxn][maxn]; int used[maxn][maxn][maxn]; int idx[maxn][maxn]; // == Graph definition == vector<int> G[maxn]; class Edge { public: int from, to, weight; Edge Edge(int f, int t, int w) : from(f), to(t), weight(w) {} }; class Node { public: int u, dist; Node Node(int u, int d) : u(u), dist(d) {} bool operator< (const Node& rhs) const { return dist > rhs.dist; } }; vector<Edge> edges; void initG _for(i, 0, maxn) G[i].clear(); edges.clear(); } void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) { edges.push_back(Edge(u, v, w)); G[u].push_back(edges.size() - 1); idx[u][v] = edges.size() - 1; } // == Graph finished == // == Dijkstra == int p[maxn]; int D[maxn], vis[maxn]; void initDij(int st) { Set(p, 0); Set(vis, 0); Set(D, inf); D[st] = 0; } void dijkstra(int st) { initDij(st); priority_queue<Node> que; que.push(Node(st, 0)); while (!que.empty()) { int x = que.top().u; que.pop(); if (vis[x]) continue ; vis[x] = 1; _for(i, 0, G[x].size()) { const Edge& e = edges[G[x][i]]; int y = e.to; if (e.weight > 0 && D[y] > D[x] + e.weight) { D[y] = D[x] + e.weight; p[y] = G[x][i]; que.push(Node(y, D[y])); } } } } // == Dijkstra finished == // == solver == int C[maxn]; void initCal Set(C, 0); } int cal initCal(); int ans = 0; _rep(st, 1, n) { dijkstra(st); _rep(v, 1, n) { if (v != st) { int u = edges[p[v]].from; used[st][u][v] = used[st][v][u] = 1; } C[st] += (D[v] == inf ? L : D[v]); } ans += C[st]; } return ans; } int del(int u, int v) { Edge& e1 = edges[idx[u][v]]; Edge& e2 = edges[idx[v][u]];; if (W[u][v].size() == 1) e1.weight = e2.weight = 0; else if (W[u][v].size() > 1) e1.weight = e2.weight = W[u][v][1]; int ans = 0; _rep(st, 1, n) { if (used[st][u][v] == 0) ans += C[st]; else { dijkstra(st); _rep(i, 1, n) ans += (D[i] == inf ? L : D[i]); } } e1.weight = e2.weight = W[u][v][0]; return ans; } // == solver finsihed == void init _for(i, 0, maxn) _for(j, 0, maxn) W[i][j].clear(); Set(used, 0); Set(idx, 0); } int main freopen("input.txt" , "r" , stdin); while (scanf("%d%d%d" , &n, &m, &L) == 3) { init(); initG(); // build graph _for(i, 0, m) { int u, v, s; scanf("%d%d%d" , &u, &v, &s); W[u][v].push_back(s); W[v][u].push_back(s); } _rep(i, 1, n) _rep(j, i + 1, n) { if (W[i][j].size()) { sort(W[i][j].begin(), W[i][j].end()); addEdge(i, j, W[i][j][0]); addEdge(j, i, W[i][j][0]); } } // build finished // solve the problem int c1 = cal(); int c2 = -1; _rep(i, 1, n) _rep(j, i + 1, n) if (W[i][j].size()) { c2 = max(c2, del(i, j)); } printf ("%d %d\n" , c1, c2); } }
Dijkstra杂题,路径输出
ceil ( x ) : = ⩾ x (离x最近的整数) \textbf{ceil}(x) := \geqslant x \textbf{(离x最近的整数)} ceil ( x ) : = ⩾ x ( 离 x 最近的整数 ) k k k 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
D ( u ) → x = D ( u ) + x K D ( u ) + x D(u) \xrightarrow{x=\frac{D(u)+x}{K}} D(u)+x
D ( u ) x = K D ( u ) + x D ( u ) + x
( K − 1 ) x = D ( u ) ⇔ x = D ( u ) K − 1 rhs = D ( u ) + x = ceil ( D ( u ) K − 1 ⋅ K ) \begin{gathered}
(K-1)x = D(u) \Leftrightarrow x = \frac{D(u)}{K-1} \\ \ \\
\text{rhs} = D(u) + x = \textbf{ceil}(\frac{D(u)}{K-1} \cdot K)
\end{gathered}
( K − 1 ) x = D ( u ) ⇔ x = K − 1 D ( u ) rhs = D ( u ) + x = ceil ( K − 1 D ( u ) ⋅ K )
run dijkstra ( ) , get D t o \text{run dijkstra}(), \ \textbf{get} \ D_{to} run dijkstra ( ) , get D t o for ∀ e ( x , y ) \textbf{for} \ \forall e(x, y) for ∀ e ( x , y ) ~~~~~~ if D ( y ) > D t o , D ( y ) = D t o , p ( y ) = e ( x , y ) \textbf{if} \ D(y) > D_{to}, D(y)=D_{to}, p(y) = e(x, y) if D ( y ) > D t o , D ( y ) = D t o , p ( y ) = e ( x , y ) ~~~~~~ if D ( y ) = D t o , ( [ x 1 , x 2 ] , y ) , x 2 < x 1 \textbf{if} \ D(y) = D_{to}, \ ([x_1, x_2], y), \ x_2 < x_1 if D ( y ) = D t o , ( [ x 1 , x 2 ] , y ) , x 2 < x 1 ~~~~~~~~~~ ( x 1 , y ) → ( x 2 , y ) , p ( y ) = e ( x 2 , y ) (x_1, y) \rightarrow (x_2, y), \quad p(y) = e(x_2, y) ( x 1 , y ) → ( x 2 , y ) , p ( y ) = e ( x 2 , y )
output path \text{output path} output path ~~~~~~ run dijkstra ( e d → s t ) \text{run dijkstra}(ed\rightarrow st) run dijkstra ( e d → s t ) ~~~~~~ out ( e d ← s t ) \text{out}(ed \leftarrow st) out ( e d ← s t ) ~~~~~~ out ( u , V ( p ( u ) ) , V ( p ( p ( u ) ) ) , ⋯ ) \text{out}(u, V(p(u)), V(p(p(u))), \cdots) out ( u , V ( p ( u ) ) , V ( p ( p ( u ) ) ) , ⋯ )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 const int maxn = 100 + 5; const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; int n, P, st, ed; // == Graph definition == vector<int> G[maxn]; class Edge { public: int from, to, isUp; Edge Edge(int f, int t, int w) : from(f), to(t), isUp(w) {} }; vector<Edge> edges; class Node { public: int u; ll dist; Node Node(int u, ll d) : u(u), dist(d) {} bool operator< (const Node& rhs) const { return dist > rhs.dist; } }; void initG edges.clear(); _for(i, 0, maxn) G[i].clear(); } void addEdge(int u, int v, int isUp) { edges.push_back(Edge(u, v, isUp)); G[u].push_back(edges.size() - 1); } // == Graph finsihed == inline int read char ch[9]; scanf("%s" , ch); if (isupper(ch[0])) return ch[0] - 'A' ; else return ch[0] - 'a' + 26; } inline char format(int u) { return u < 26 ? 'A' + u : 'a' + (u - 26); } inline bool isUp(int u) { return u < 26 ? 1 : 0; } // == dijkstra == ll D[maxn]; int vis[maxn]; int pid[maxn]; void initDij(ll P, int st) { _for(i, 0, maxn) D[i] = inf; D[st] = P; Set(vis, 0); Set(pid, 0); pid[st] = -1; } void dijkstra(ll P, int st) { initDij(P, st); priority_queue<Node> que; que.push(Node(st, P)); while (!que.empty()) { int x = que.top().u; que.pop(); //debug(D[x]); if (vis[x]) continue ; vis[x] = 1; _for(i, 0, G[x].size()) { const Edge& e = edges[G[x][i]]; int y = e.to; ll d_to; if (e.isUp) d_to = (ll)ceil(D[x] * 1.0 / 19 * 20); else d_to = D[x] + 1; //debug(d_to); if (D[y] > d_to || (D[y] == d_to && format(x) < format(edges[pid[y]].from))) { D[y] = d_to; pid[y] = G[x][i]; que.push(Node(y, D[y])); } } } } void print (int u) { if (pid[u] == -1) { printf ("%c\n" , format(u)); return ; } printf ("%c-" , format(u)); print (edges[pid[u]].from); } // == dijkstra finsihed == int main freopen("input.txt" , "r" , stdin); int kase = 0; while (scanf("%d" , &n) == 1 && n >= 0) { initG(); printf ("Case %d:\n" , ++kase); // build graph _for(i, 0, n) { int u = read (); int v = read (); if (u != v) { addEdge(u, v, isUp(u)); addEdge(v, u, isUp(v)); } } // graph finished // then dijkstra scanf("%d" , &P); st = read (); ed = read (); //debug(ed); dijkstra(P, ed); printf ("%lld\n" , D[st]); print (st); } }